polarimeter chirality|polarimetry explained : purchaser Rotation of plane polarized light by a chiral compound is known as optical activity. Achiral compounds are optically inactive. Racemic mixtures are optically inactive because the . Sweet femboys. 11 955 subscribers. Admin предложка: https://t.me/ilyaleny. Send your pic: https://t.me/Simpf13f. Discord: https://discord.gg/6C9GMwbp. Chat: .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Casino.guru is an independent source of information about online casinos and online casino games, not controlled by any gambling operator. All our reviews and guides are created honestly, according to the best knowledge and judgement of the members of our independent expert team; however, they .
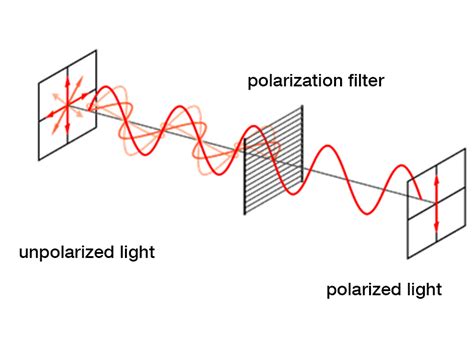
polarimetry wiki
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course.Rotation of plane polarized light by a chiral compound is known as optical activity. Achiral compounds are optically inactive. Racemic mixtures are optically inactive because the .A test for achirality is the presence of a mirror plane within the molecule. If a molecule has a plane within it that will cut it into two symmetrical halves, then it is achiral. Therefore, lack of such a plane indicates a molecule is chiral. . Polarimetry. updated. Most physical properties of enantiomers i.e., melting point, .
To check the chirality of a chiral compound, the specific rotation is measured on the polarimeter, using a specified solvent. Then can the specific rotation result be used for confirmation of the R or S configuration of the .A polarimeter[1] is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. [2] Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample.
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking .A polarimeter is an instrument that allows polarized light to travel through a sample tube containing an organic compound and the degree to which an organic compound rotates plane-polarized light is measured. . This is because both right hand and right glove are chiral. A chiral object only fit into a specific chiral environment.A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules).. Operation Principle .One enantiomer of these chiral compounds is dextrorotatory; the other is levorotatory. To decide whether a compound should be optically active, we look for evidence that the molecules are chiral. The instrument with which optically active compounds are studied is a polarimeter, shown in the figure below.
T he sample containing a chiral compound rotates the plane of polarization of plane-polarized light, and the direction and angles of the rotation depend on the nature and concentration of the chiral substances. The rotation angles can be measured using a polarimeter (later in this section). For a pair of enantiomers with the same concentration, under the same conditions, . Here, a flexible, filter-less full-Stokes polarimeter featuring a uniaxial-oriented chiral perovskite film is first reported. It is found that, the strategic manipulation of the surfactant-mediated Marangoni effect during blade coating, is crucial for guiding an equilibrious mass transport to achieve oriented crystallization. An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with plastic interlocking toy bricks, such as Lego bricks. The instrument was used to demonstrate the optical rotation of plane polarized light as .
Here is a diagram of a modern polarimeter. Image source: wikipedia . Chirality 2008, 20 (1), 5-19 DOI: 1002/chir.20494 Another historical review discussion Pasteur’s life and his work on the fundamentals of chirality in organic chemistry. A model for optical rotation L. L. Jones and Henry Eyring Here, the anisotropy of chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is explored and the full-Stokes polarimeter based on pure chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is reported. By using optical anisotropy .
Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample. Rotation is given in +/- degrees, depending on whether the sample has d- (positive) or l- (negative) enantiomers.
Chirality and optical activity: . This is the origin of the phenomenon known as optical rotation, which is measured using a polarimeter. Measuring optical rotation as a function of wavelength is termed optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) spectroscopy. Circular birefringence:the orange cuboid represents the sample .
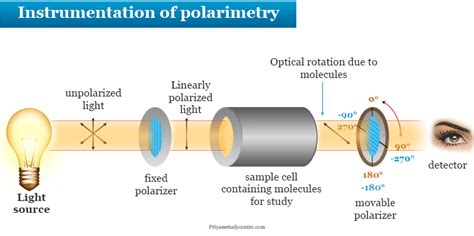
Here, the anisotropy of chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is explored and the full-Stokes polarimeter based on pure chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is reported. By using optical anisotropy and the ability to distinguish the helicity of the circularly polarized light, chiral 2D perovskite polarimeter integrates the polarizer, waveplate .
This study provides a paradigm to construct filterless on-chip Stokes polarimeter with great simplicity and low cost and explores the anisotropy of chiral 2D perovskite single crystals. Full-Stokes polarimeters, equipped with the capability of discriminating light polarization states, can find important applications in various optical and optoelectronic devices. Nevertheless, .A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the laboratory component of the course. . Chiral organic compounds isolated from living organisms are usually optically active, indicating that one of the . The concepts of steroisomerism and chirality command great deal of importance in modern organic chemistry, as these ideas helps to understand the physical and theoretical reasons behind the formation and structures of .Racemisation, Optical activity & Chirality in Organic Chemistry - Racemisation is the transformation, by heat or chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into an optically inactive. Learn about Chirality, .
Typically included in the discussion of chirality is the use of a polarimeter to determine the optical rotation of chiral compounds. Although the theory behind polarimeters is quite simple, we have found that undergraduate students often have a difficult time conceptualizing how the angle of rotation of polarized light is measured in practice.
polarimetry techniques
A polarimeter is a device that measures the rotation of linearly polarized light by an optically active sample. This is of interest to organic chemists because it enables differentiation between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., enantiomers. Enantiomers, chiral molecules, are molecules which lack an internal plane of symmetry and have a non-superimosable mirror image. One .Optical activity is a property unique to chiral substances. For example 2-butanol, which possess a chiral center (one carbon bound to four different ligands). . Polarimeter Light Sources. It is now common practice to use other light sources such as xenon or tungsten halogen. With appropriate filters, these light sources offer advantages of .
The geometrical property of a molecule that is analyzed with a polarimeter is called chirality; hence molecules with mirror-image geometries are called chiral. They cannot be superimposed on their mirror image. The mirror images are called left- and right-handed enantiomers. Chiral molecules are typically organic molecules and biomolecules . Here, the anisotropy of chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is explored and the full-Stokes polarimeter based on pure chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is reported. By using optical anisotropy and the ability to distinguish the helicity of the circularly polarized light, chiral 2D perovskite polarimeter integrates the polarizer, waveplate .The geometrical property of a molecule that is analyzed with a polarimeter is called chirality; hence molecules with mirror-image geometries are called chiral. They cannot be superimposed on their mirror image. The mirror images are called left- and right-handed enantiomers. Chiral molecules are typically organic molecules and biomolecules . Here, the anisotropy of chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is explored and the full-Stokes polarimeter based on pure chiral 2D perovskite single crystals is reported. By using optical anisotropy and the ability to distinguish the helicity of the circularly polarized light, chiral 2D perovskite polarimeter integrates the polarizer, waveplate .
In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. . observed rotation is a result of the different components of the plane polarized light interacting differently with the chiral center. In order to observe the maximum . The ability to detect the full-Stokes polarization of light is vital for a variety of applications that often require complex and bulky optical systems. Here, we report an on-chip polarimeter comprising four metasurface-integrated graphene-silicon photodetectors. The geometric chirality and anisotro .For instance, the sugar solution exhibits optical rotation when observed through a polarimeter because it is optically active. This property arises from an interaction of the electromagnetic radiation of polarized light with the unsymmetric electric fields generated by the electrons in a chiral molecule.
Recording optical rotation with a polarimeter: The plane of polarisation of plane polarised light (4) rotates (6) as it passes through an optically active sample (5).This angle is determined with a rotatable polarizing filter (7).. In chemistry, specific rotation ([α]) is a property of a chiral chemical compound. [1]: 244 It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane .
charpy impact test instron
Resultado da If you don’t know what a blocking bet is, here’s the situation. You find yourself on the river with a weak-to-medium strength hand, and it’s on you to act first. You desperately want to get to showdown because you might have the best hand, but your hand isn’t strong enough to call a huge bet so you’re afraid .
polarimeter chirality|polarimetry explained